We frequently concentrate on exercises that enhance cardiovascular health, increase muscular strength, and increase endurance in our pursuit for physical fitness and general well-being. The durability and effectiveness of our respiratory muscles are one facet of our health that is commonly disregarded. We may exercise our respiratory muscles for greater functioning in the same way that we train our other muscles for strength and endurance. The role of a respiratory muscle trainer is now clear.
Understanding the Respiratory System
Before delving into the myriad benefits of a respiratory muscle trainer, it’s paramount to grasp the intricacies of our respiratory system. The respiratory system serves as the vital bridge for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between our bodies and the external environment. At the epicenter of this exchange lie our lungs, fortified by an intricate network of respiratory muscles.
Among these muscles, the diaphragm takes center stage, while the intercostal muscles and a cohort of auxiliary muscles play pivotal roles in the symphony of respiration.
It’s important to note that these respiratory muscles, akin to any other muscle group in our body, can be strengthened and honed through targeted exercises and training. This enhancement not only elevates our understanding of respiratory physiology but also augments our overall well-being.
The Importance of Respiratory Muscle Strength
- Better Lung Function: The capacity and effectiveness of the lungs are increased by strong respiratory muscles. Better blood oxygenation and carbon dioxide elimination are made possible as a result, both of which are essential for general health and performance.
- Increased Endurance: Stronger respiratory muscles enable athletes and fitness enthusiasts to work out for longer periods of time and at higher intensities without becoming exhausted.
- Improved Respiratory Efficiency: Breathing requires less effort when the respiratory muscles are strong. This can increase overall energy levels and lessen sensations of being out of breath while engaging in physical activity.
- Improved Posture and Core Stability: Proper breathing practises, frequently linked to respiratory muscle training, encourage improved posture and core stability, which lowers the risk of musculoskeletal problems.
Introducing the Respiratory Muscle Trainer
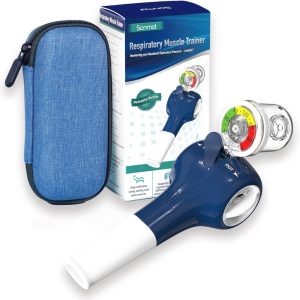
To specifically target and develop the respiratory muscles, a respiratory muscle trainer (RMT) is a device. Usually, it comprises of a portable gadget with a mouthpiece and a resistance setting that may be adjusted. An RMT works on a straightforward premise: by forcing the respiratory muscles to work harder by inhaling and exhaling against resistance, the muscles’ strength and endurance are subsequently increased.
Benefits of Using a Respiratory Muscle Trainer
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Athletes and other active persons perform better when their muscles are supplied with oxygen more efficiently during activity.
- Quicker Recovery and Less Muscular Soreness: By lessening feelings of weariness during and after exercise, stronger respiratory muscles contribute to a quicker recovery and less muscular soreness.
- Respiratory problems: For those with respiratory disorders including asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), an RMT can be a helpful tool for managing symptoms and improving general lung function.
- Tension Reduction: Because deep, regulated breaths are known to have relaxing benefits, RMT breathing methods can help lower tension and anxiety levels.
- Posture and Core Stability: Regular RMT use can improve posture and core stability, which lowers the likelihood of back discomfort and associated problems.
How to Use a Respiratory Muscle Trainer
Using an RMT is relatively straightforward:
- To start, set the resistance at a modest level, and as you feel comfortable with the initial resistance setting, move on to the next adjustment of resistance, and so on.
- Breathe in and out via the device while standing or sitting upright.
- Engage in consistent practise, ideally as part of your warm-up or cool-down regimen.
- For advice on adding RMT into your exercise routine, speak with a healthcare practitioner or fitness trainer.
- During the training session, you can even alter both the inhale and exhale dials to any resistance levels based on your preference (it is not mandatory that both the dials be equal).
NOTE: You can perform targeted inspiratory muscle training by inhaling through the Respiratory Muscle Trainer (mouth) and exhaling through the nose, and the vice versa applies to targeted expiratory muscle training.
According to a study that was written up in the 2022 issue of the journal Respiratory Medicine, using a respiratory muscle trainer (RMT) for 12 weeks led to significant gains in exercise capacity, quality of life, and respiratory function. The research also revealed a decreased risk of respiratory infections in those who used RMTs.
The majority of the studies points to the health benefits of using a respiratory muscle trainer on a daily basis. RMT has been demonstrated to benefit persons with a range of illnesses, such as COPD and asthma, by enhancing their capacity for exercise, quality of life, and lowering their risk of respiratory infections.
An effective tool for improving lung health, sports performance, and general wellbeing is a respiratory muscle trainer. Including RMT in your regimen may be a game-changer whether you’re an athlete looking for top performance or someone looking to enhance your respiratory health.












Leave a reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.